Abstract
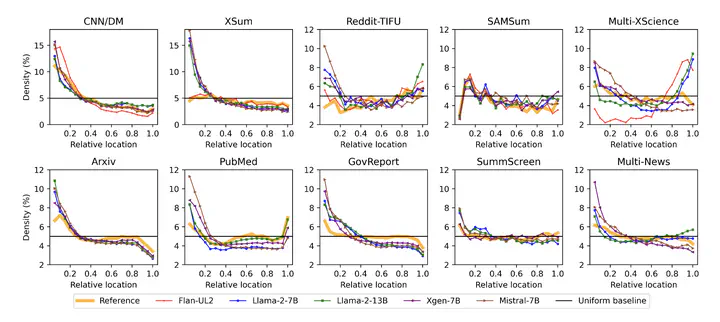
Large language models (LLMs) excel in zero-shot abstractive summarization tasks, delivering fluent and pertinent summaries. Recent advancements have extended their capabilities to handle long-input contexts, surpassing token limits of 100k. However, in the realm of multi-document question answering, language models exhibit uneven utilization of their input context. They tend to favor the initial and final segments, resulting in a U-shaped performance pattern concerning where the answer is located within the input. This bias raises concerns, particularly in summarization tasks where crucial content may be dispersed throughout the source document(s). This paper presents a comprehensive investigation encompassing 10 datasets, 5 LLMs, and 5 evaluation metrics to analyze how these models leverage their input for abstractive summarization. Our findings reveal a pronounced bias towards the introductory content (and to a lesser extent, the final content), posing challenges for LLM performance across a range of diverse summarization benchmarks.